Chapter 4 Review Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
Atomic number and mass number are always whole numbers because they are obtained by counting whole objects (protons, neutrons, and electrons). The sum of the mass number and the diminutive number for an cantlet (A-Z) corresponds to the full number of subatomic particles present in the atom. The mass number reports the mass of the atom'south nucleus in diminutive mass units (amu).
Table of Contents
- Atomic number
- Recommended Videos
- What is Atomic Number?
- What is the Mass Number?
- History of Atomic Number
- Examples of Diminutive Number
- Atomic Number Orbital Energy Levels
- Difference betwixt Valency, A and Z
- Solved Instance
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Diminutive Number
The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons in it, and it is used to differentiate 1 element from another. The mass number of an element is determined by the number of protons and neutrons combined.
The modernistic periodic table is arranged in such a way that all the elements have an increasing atomic number, and after, increasing mass number. Only exercise you know what mass number, or even what diminutive number is?
Well, equally you know, an atom consists of electrons, protons and neutrons. The number of electrons in the outermost shell gives usa the valency of the cantlet. Similarly, the number of protons and neutrons are associated with the atomic number and mass number of the atom.
Recommended Videos

Allow's expect at the difference between the two terms.
What is Atomic Number?
- The total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom gives us the atomic number of that atom.
- It is represented with the letter 'Z.'
- All the atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons, and hence the same atomic number.
- Atoms of unlike elements have unlike atomic numbers.
- For example, all carbon atoms have the atomic number of 6, whereas all atoms of Oxygen have 8 protons in their nucleus.
What is Mass Number?
- The number of protons and neutrons combined to give united states the mass number of an atom.
- Information technology is represented using the letter of the alphabet 'A.'
- As both protons and neutrons are present in the nucleus of an atom, they are together called nucleons.
- For example, an atom of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Thus, its mass number is 12.
- While the number of protons remains the same in all atoms of an element, the number of neutrons can vary. Thus, atoms of the same element tin have different mass numbers, and these are called isotopes.
- The weight of an electron is almost negligible. Thus, the atomic mass of an atom is almost the same equally its mass number.
History of Atomic Number
We take the beingness of atoms for granted – yet for centuries no ane believed in them. Around 2500 years ago a Greek philosopher called Leucippus and his student Demokritos put forrard the thought that the universe is made upwardly of tiny indivisible particles, which they called atoms. Unfortunately the cracking Greek philosopher Aristotle did not agree with them. As Aristotle views were accepted throughout Europe for almost 2000 years the idea of atoms was shelved for centuries to come.
Atoms are the building blocks of matter. They combine in numerous patterns and form dissimilar substances. All atoms except the common grade of hydrogen contain protons, neutrons and electrons. The diminutive number of an element is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons in shells that is the energy level around the nucleus.
Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number only distinct neutron numbers, and hence distinct mass numbers. The average isotopic mass of an isotopic mixture for an element in a defined environment on Earth determines the element'south standard atomic weight. A trivial more than three-quarters of naturally occurring elements be as a mixture of isotopes, and the average isotopic mass of an isotopic mixture for an chemical element in a defined environment on Earth determines the chemical element'south standard diminutive weight.
Examples of Atomic Number
The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom or the number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom.
Atomic number = Number of protons
For example, in a sodium cantlet, there are 11 electrons and xi protons. Thus the atomic number of Na cantlet = number of electrons = number of protons = xi.
Atomic Number Orbital Energy Levels
When an electron is at a specific free energy level, it is more likely to be found in certain portions of that level than others. Orbitals are the name for these sections. Sublevels are made upward of orbitals with the same energy. A maximum of two electrons can exist found in each orbital.
The almost common way of showing the organization of electrons in an atom is to draw diagrams similar those shown in the diagram.
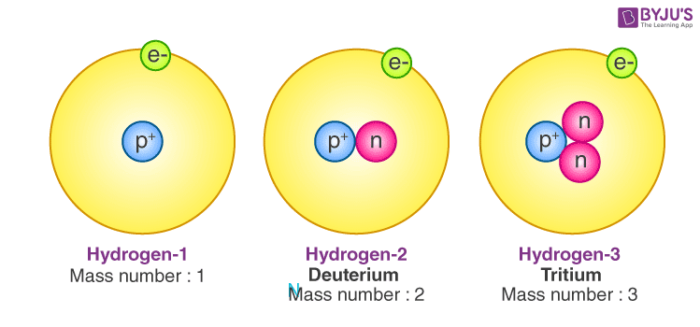
To write down the numbers of electrons in each energy level. The atomic number of an element tells us how many electrons there are in the atoms. For example, the atomic number of carbon is 6 giving us six electrons equally 2,4. So an atom with the atomic number 12 has an electronic structure 2, 8, two, with two electrons in the inner energy level, then 8 in the next energy level and 2 in the outer highest energy level. The simplest mode to understand these arrangements is to await at lots of examples of them.
Departure between Valency, A and Z:
When we desire to discover out the valency, we look at electrons only in the outermost shell of the atom. But when we want to know the atomic number or the mass number, we wait at the full number of protons and neutrons.
i. Notation of Cantlet
To write the notation of an cantlet, we need to know the symbol of the element, the atomic number and the mass number. The mass number of the cantlet goes above the symbol and the atomic number is written as a subscript.
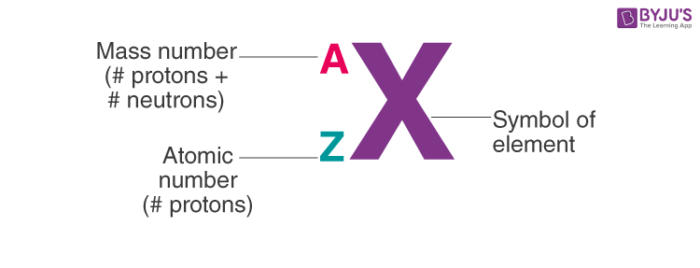
So, the notation of Carbon is:
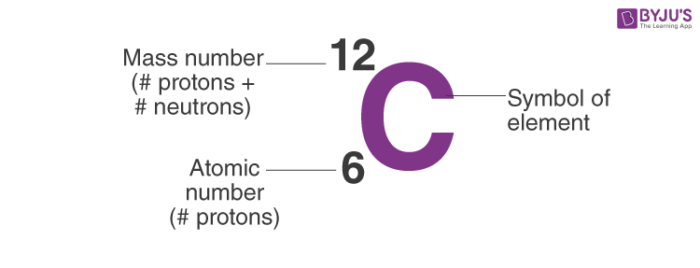
two. Calculating Number of Neutrons:
If we know the number of protons and the mass number of an element, we tin can also summate the number of neutrons simply by subtracting its atomic number from its mass number.

Solved Instance
Question:
An atom has an atomic number of ix and a mass number of 19.
- Determine the number of protons present
- Determine the number of neutrons present
- Determine the number of electrons present
Solution:
- There are 9 protons because the atomic number is ever equal to the number of protons present.
- In that location are 10 neutrons because the number of neutrons is e'er obtained by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
(protons + neutrons) – protons = neutrons - At that place are ix electrons because the number of protons and the number of electrons are ever the same in an cantlet.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Who discovered the atomic number?
The number of protons (positive charges) in the nucleus of an atom is given by its atomic number. This term was first introduced past Henry Gwyn-Jefferies Moseley.
How exercise you find atomic mass from the atomic number and the number of neutrons?
Add the mass of protons and neutrons to calculate the atomic mass of a unmarried atom of an element. The number of protons and the number of neutrons together determine the mass number of an element: mass corporeality = protons + neutrons.
Why the atomic number is denoted by Z?
The atomic number symbol, Z, stands for "Zahl," meaning German number. The symbol Z denoted an element's place in the periodic tabular array before 1915.
What is the mass number?
The consummate corporeality in the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. For example, nitrogen has seven protons in its nucleus and seven neutrons, supplying information technology with 14 masses.
What is an atomic number and mass number?
The mass number in a nucleus is the combined number of protons and neutrons, then it'due south protons and neutrons, and A symbolizes it. So A is the number of masses, which is equal to the number of protons, that is the number of atoms that nosotros symbolized by Z, plus the number of neutrons.
To know more about the number of protons, neutrons and isotopes, download BYJU'Southward – The Learning App.
Source: https://byjus.com/chemistry/atomic-number-mass-number/
0 Response to "Chapter 4 Review Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms"
Post a Comment